Cordyceps
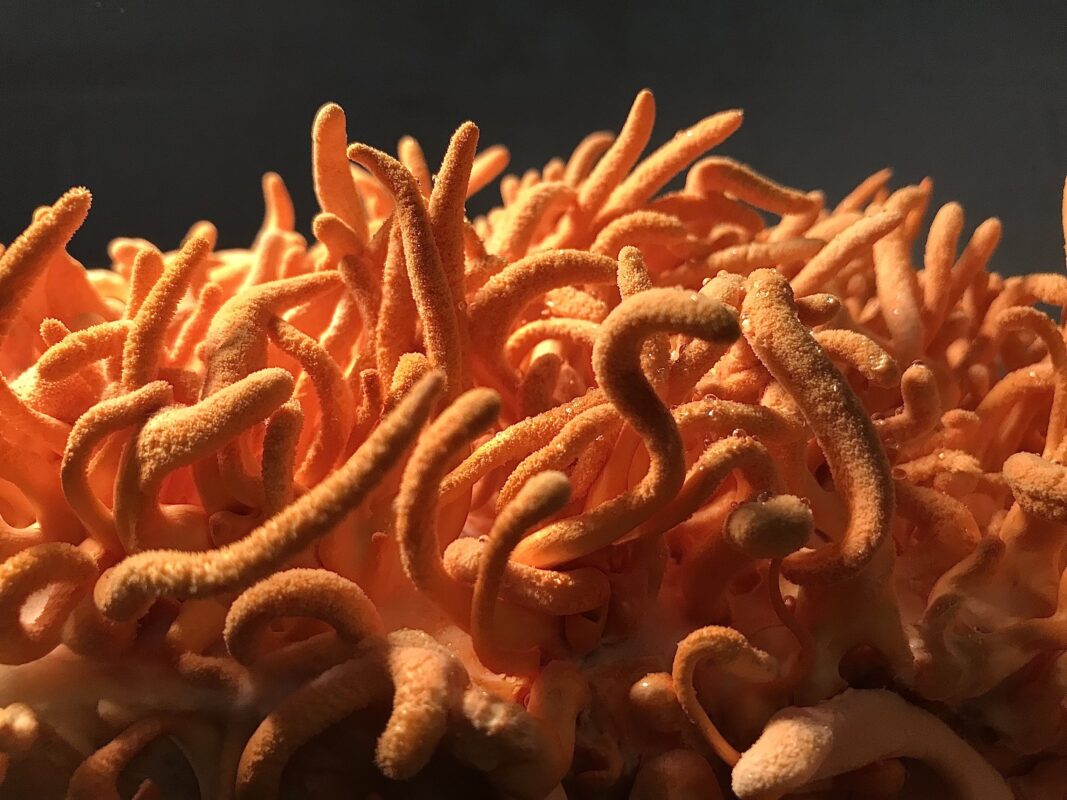

Cordyceps militaris (Military cordyceps, Caterpillar fungus)
Description
Cordyceps militaris is a parasitic fungus that primarily preys on insect larvae. Once the fungus consumes the insect, it produces an elongated fruiting body, which is the part often used in medicinal applications. The fruiting body is bright orange or red, and it is significantly smaller than its more famous cousin, Cordyceps sinensis, which preys on caterpillars in the Tibetan plateau.
Nowadays Cordyceps mushrooms are cultivated on grain substrates in labs and are more potent than the Cordyceps sinensis found in the wild.
History of traditional use
Traditionally used in many Asian countries, especially China and Korea, Cordyceps militaris has been prized for its purported ability to restore energy, enhance stamina, and reduce fatigue.
One of the most frequently described “side effects” described by those who use Cordyceps is its aphrodisiac and sexual potentiator qualities for both men and women.
Nutritional and Active Molecular Profile
Health benefits
Symptoms It can help relieve
Fatigue, shortness of breath, reduced athletic performance, and more.
Possible cautions/interactions
Cordyceps might slow blood clotting, so there is a potential risk of bleeding in people with bleeding disorders. It may also interfere with medications that slow blood clotting (like anticoagulants and anti platelet drugs). As with any supplement, consult a healthcare professional before use, especially if taking medications or have underlying health conditions.
State of current scientific research
Research on Cordyceps militaris is ongoing. While its use have been known for its medicinal properties in Asia for at least 2000 years, further rigorous research on humans is required to ascertain the full extent of its benefits and possible side effects.
Online articles
regenerative protocol
mushroom